What is a Data Analyst? Everything You Need to Know

 Written by:
Written by:Nathan Rosidi
What is a data analyst, and what is their role in data teams? What does it take to be a data analyst? Here, we explore this attractive data role further.
Do you know how much data is created every day? According to Exploding Topics, 328.77 million terabytes of data are generated daily. I don’t even know how to get this quantity into comprehensible measures.
Let’s try it like this. My computer’s hard drive is 500 GB or 0.5 TB, a decent size for daily use. Every day, more than 650 millions of my hard drives full of data is produced! Millions. Every. Single. Day.
Businesses employ data analysts to make sense of this overwhelming quantity of data. Let’s examine how these data professionals do their work and how you can become one of them.
What is a Data Analyst?
Data analysts bridge the gap between raw data and strategic decision-making. Nowadays, you can find these data professionals in every department and industry: marketing, finance, operations, legal, human resources, inventory, risk management, you name it.
They analyze data relevant to their department and company to extract valuable information. By doing this, they provide management with something more than a hunch on which to base strategic decisions.
Role of a Data Analyst in Businesses and Organizations
Data analysts provide various aspects of data insights, which adds a multidimensional aspect to the role.
It’s difficult to include all the possible ways data analysts contribute to companies. However, here are the most typical ones:
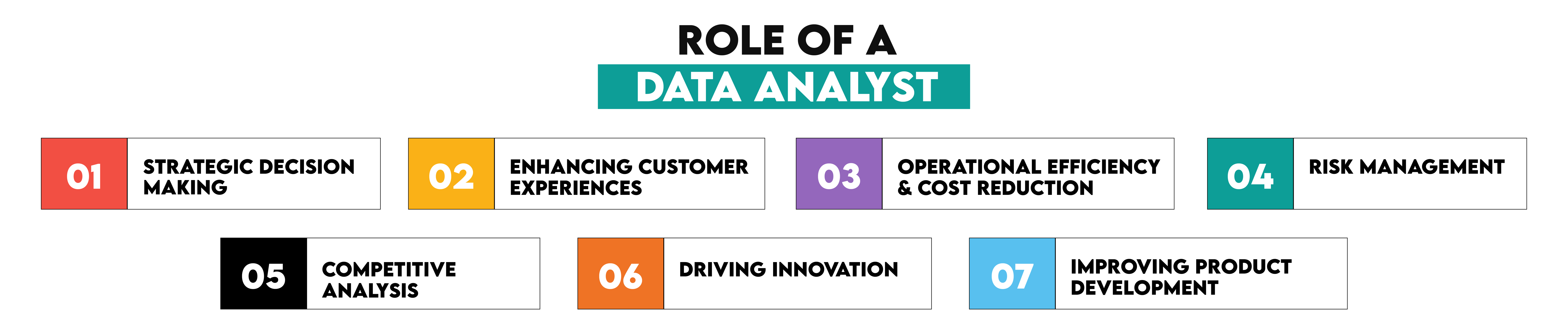
1. Strategic Decision Making: Data analysts' insights help management make informed decisions. These insights can identify new market opportunities, understand customer preferences, and discover new marketing strategies.
2. Enhancing Customer Experience: Data analysis can uncover patterns and trends in customer preferences and behavior. With this info, products, services, and marketing campaigns that better suit customer needs can be created. This, in turn, can lead to improving customer satisfaction and loyalty and getting new customers.
3. Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction: Data analysts can help improve a company’s efficiency by identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the operational process. Their insights help in streamlining operations and optimizing resource allocation. Thus, they improve productivity and reduce costs, which impacts the company’s profitability.
4. Risk Management: Analyzing data also can be used in risk management. In that context, data analysts help identify and mitigate risks.
5. Competitive Analysis: Data analysts’ skills can also be used to understand better the company’s market, which includes competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, market share, and strategies. This helps a company position themselves in the market.
6. Driving Innovation: Data analysts have the power to turn a reactive company into a proactive player. In their analysis, they can predict future market and customer development. With this, they enable a company to innovate and benefit from being a market pioneer.
7. Improving Product Development: By understanding customer and market needs, data analysts can give directions on product features, design, and functionality refining. This, of course, improves the product’s success.
Data Analysis Process
Once you understand the data analysis process, it’ll be easier to understand what data analysts do to fulfill their role.
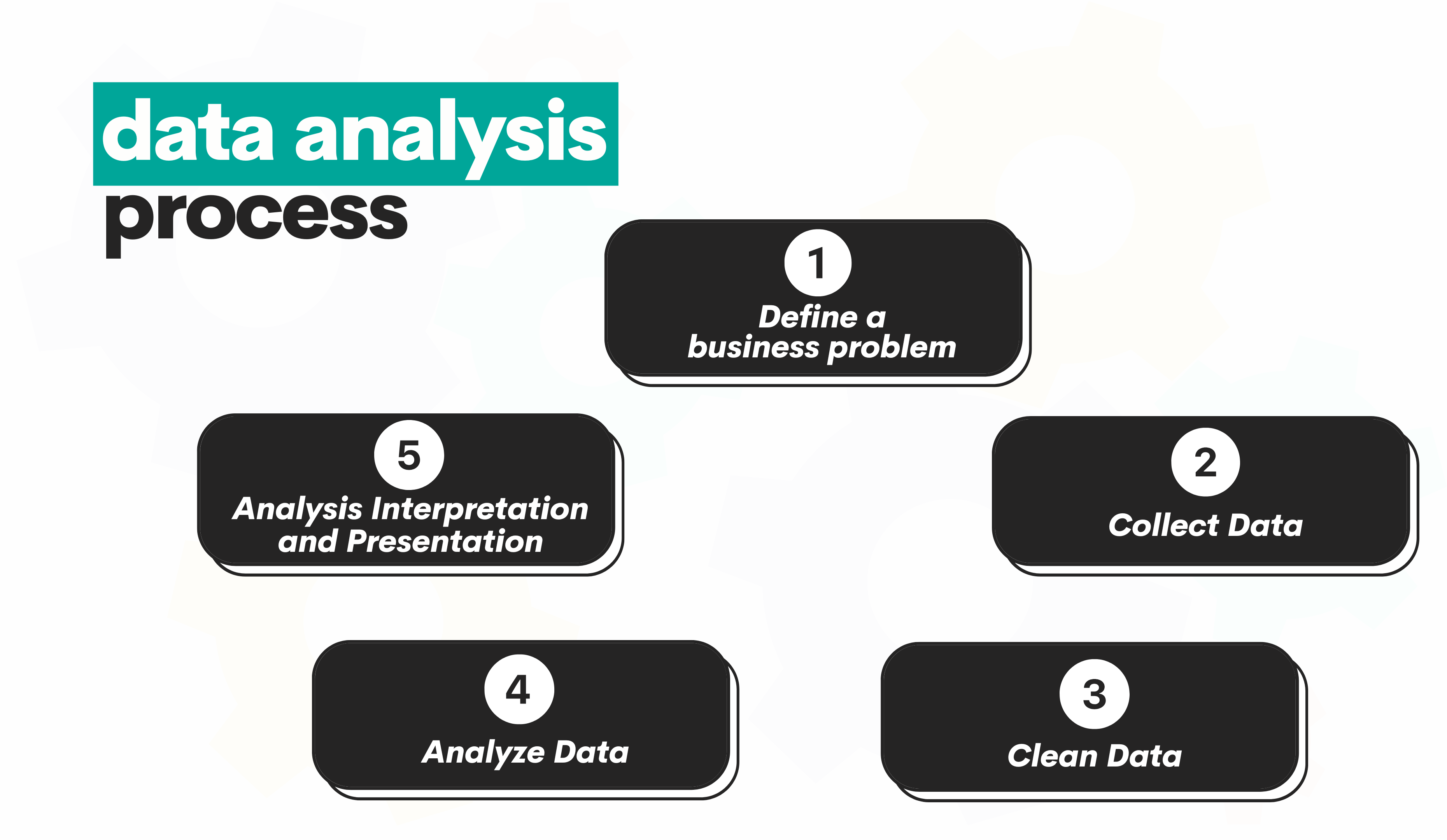
Data analysis starts by defining a business problem and analysis objectives. In other words, what are you trying to achieve with your analysis? This step will give you the necessary (business) direction for the entire analysis process.
To do an analysis, you first need to have data in the first place. Data analysts usually collect data from various sources, such as internal databases, external datasets, online surveys, and public data repositories. The point is not only to collect data but also for it to be relevant and of the highest quality possible.
Cleaning data can improve its quality and suitability for analysis. In most cases, this encompasses standard tasks, such as handling missing values, removing duplicates, correcting errors, and standardizing data formats. This is crucial for your analysis’s reliability and accuracy.
Now comes the stage you’ve been waiting for so long: analyzing data. This involves first performing the Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) to get an overall sense of your data, such as its structure, detecting outliers, understanding distributions, and finding patterns and anomalies. After that, you will apply statistical methods and other analytical techniques (sometimes, but rarely, machine learning techniques) to uncover insights, trends, relationships, and patterns within your data, which is the essence of data analysis.
Once done with that, you need to interpret the results and present them to stakeholders. Interpretation means finding insights: understanding analysis results, their implications, and determining their significance in relation to the analysis objective. These insights need to be presented in an understandable manner. This usually means creating reports, dashboards, data visualizations, and presentations.
Data Analyst's Job Responsibilities
From the above list, it’s easy to deduct the data analyst’s day-to-day responsibilities, as shown in the overview below.
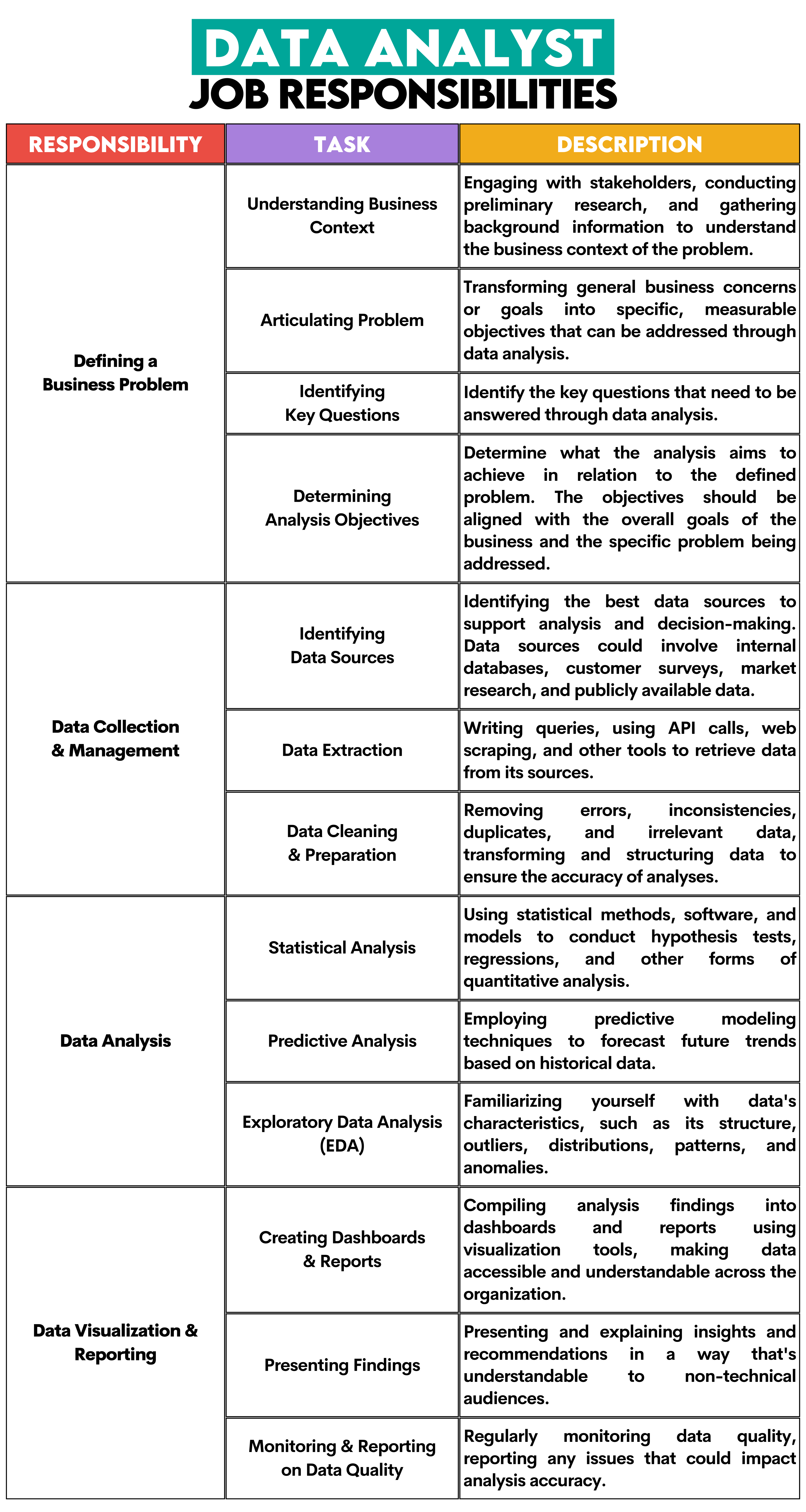
This is all in theory. Practice rarely follows it to the point. What of these tasks will be a part of a data analyst’s job and to what extent it heavily depends on the company, its size, and organizational structure?
Some more realistic accounts of the data analyst’s job can be found in the r/analytics subreddit. More precisely, in the Data Analysts: Walk Me Through a Typical Day thread.
I especially like the response in the reply marked as the best reply, as it closely matches my experience, too. In the user’s words:
25% meetings: team meetings for status updates or presentations, 1:1 with my boss, or meeting with stakeholders (in my case, product managers) to understand what questions I can answer for them using data or review data collection requirements
25-50% writing queries in SQL or understanding how the data is collected (my product is a website so looking at what analytics tags fire as I click different things on the site)
25-50% analysis - using Excel, Tableau or Python to explore the data via charts and visuals and begin to form insights which are usually summarized in a PowerPoint.
Skills Required to Become a Data Analyst
As with most data jobs, data analysts, too, need to have a good balance between technical and soft skills.
Technical Skills
These five technical skills are inescapable if you want to become a data analyst.

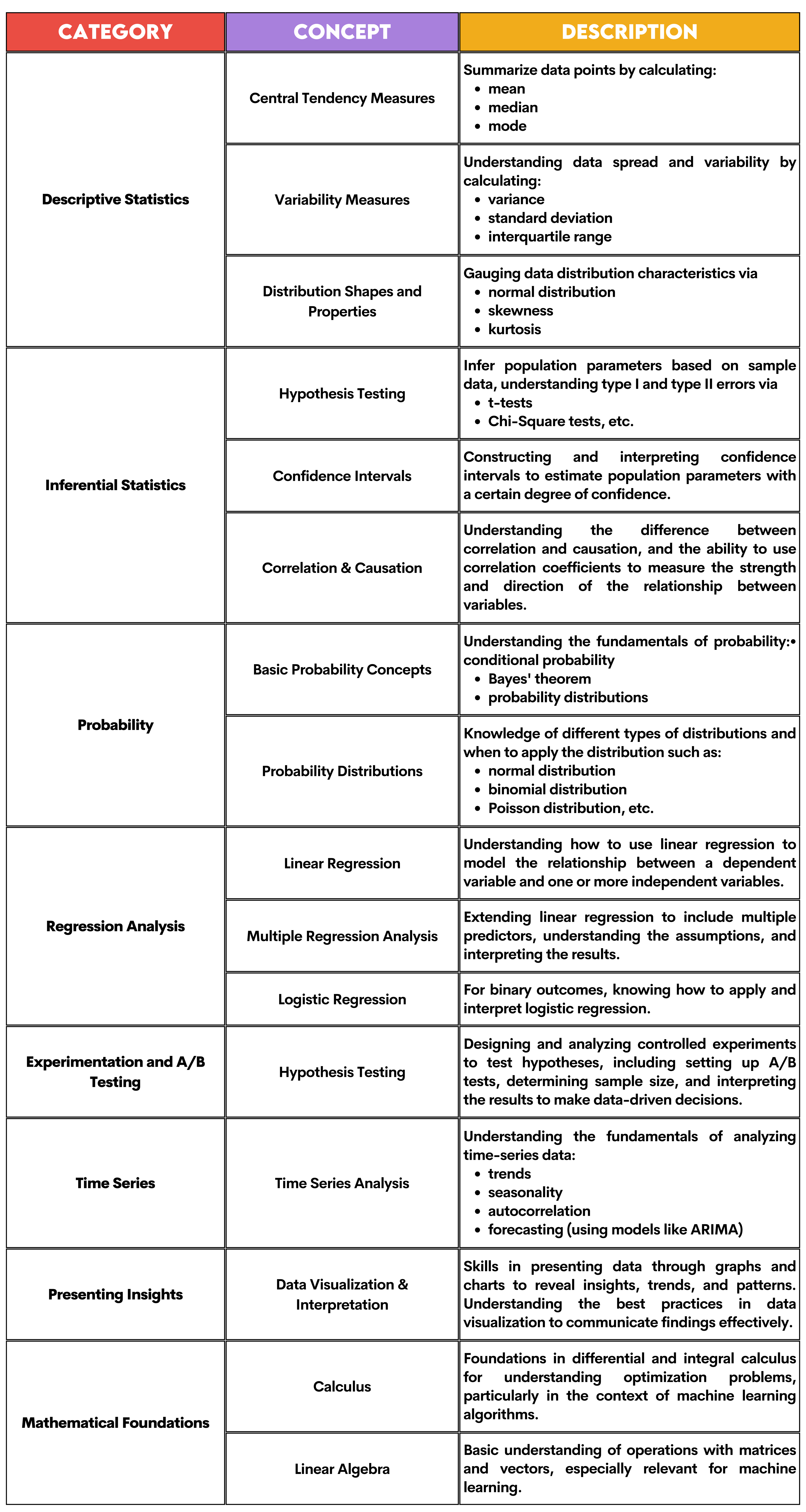
1. Statistical Analysis & Mathematics
In a data analyst job, understanding statistical tests, distributions, and probability is crucial, as these concepts form the backbone of data analysis.
Also, knowledge of mathematical concepts helps in creating models that can predict outcomes and analyze trends.
Here are more details on some concepts data analysts need to know.
2. Programming Languages
Data analysts most often use these programming languages.
- SQL: A must for data analysts! SQL is essential for extracting and manipulating data stored in relational databases. You can find more about this in our article, which explains the SQL skills required for data analyst.
- Python & R: Nice to have for most data analyst jobs. However, proficiency in these languages gives you another level of data manipulation, analysis, and visualization through some of the most common libraries:
Also, don’t forget a good old Excel! While not a programming language, you’ll probably use it for many of your tasks. Whisper it, but it’s, in many cases, still an ultimate data analysis tool.
3. Data Visualization
This skill refers to using data visualization tools (e.g., Tableau, PowerBI, or Excel) or Python/R libraries to create insightful visuals and dashboards that can communicate findings to non-technical stakeholders.
4. Data Cleaning and Preparation
These skills mean removing inaccuracies, handling missing values, and preparing data for analysis are crucial, as clean data is a prerequisite for accurate analysis.
5. Data Warehousing and Big Data Technologies
Depending on the particular job description, it might be beneficial to know a little something about data warehousing and big data. This means at least some fundamental use of data warehousing solutions (e.g., Amazon Redshift or Google BigQuery) and big data platforms (e.g., Hadoop or Spark).
Soft Skills
The soft skills are similar for most data jobs, including data analysis.
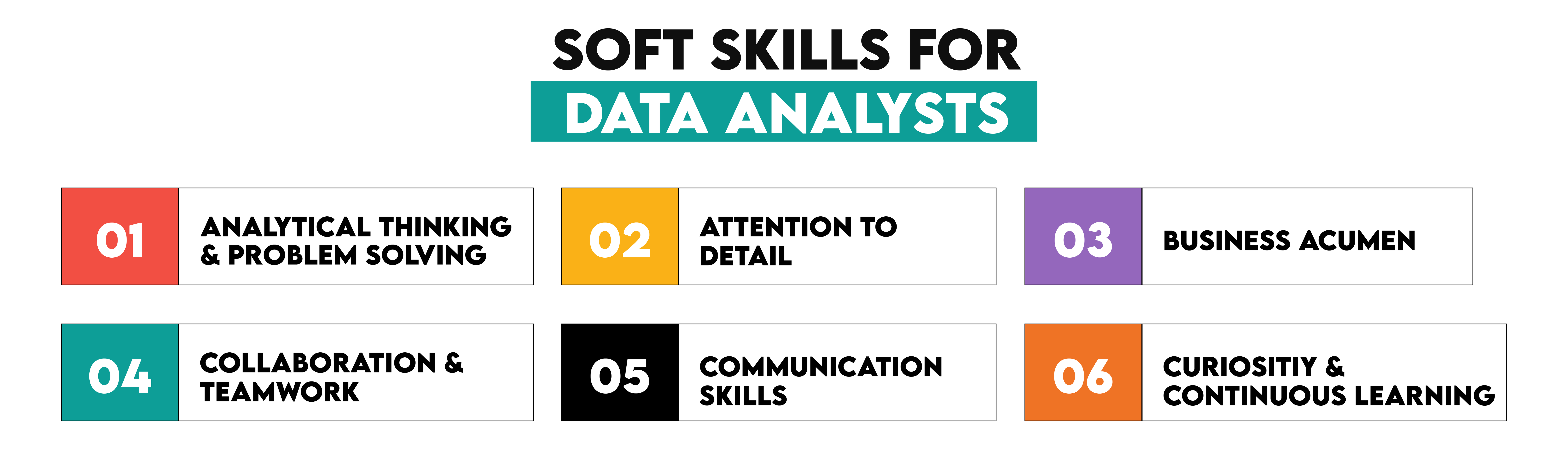
1. Analytical Thinking and Problem-Solving
The ability to think critically, identify patterns, and solve complex problems means you’ll be able to make sense of data and statistical evidence.
2. Attention to Detail
In data analysis, precision is the key. Small errors can lead to incorrect conclusions. If you’re attentive to detail, this will ensure your analysis is accurate and reliable.
3. Business Acumen
Remember, data analysis starts with formulating a business problem it wants to solve. So, understanding business fundamentals, industry-specific knowledge, and the ability to link data insights with business objectives to provide actionable recommendations is an essential skill for data analysts.
4. Collaboration and Teamwork
Data analysts often work in teams and must collaborate with other departments or stakeholders. Being a team player and having the ability to work well with others is important for success.
5. Communication Skills
Connected to the above point, you’ll have to communicate with other people when collaborating, whether you want to or not. Strong verbal and written communication skills are essential for explaining technical concepts and findings to non-technical audiences, writing clear reports, and presenting data visually.
6. Curiosity and Continuous Learning
The field of data analysis is rapidly evolving. Hence, a strong desire to learn and stay updated with the latest tools, techniques, and best practices is essential.
The Difference Between a Data Analyst and Other Data Roles
The above responsibilities and tasks overlap with some other data team members. This sometimes makes it difficult to differentiate data analysts from other job descriptions. They are most often conflated with data scientists, business analysts, and BI analysts.
Let’s look at what makes data analysts different from those three data jobs.
The best way to find the differences between the two jobs is by comparing their educational background, scope of work, job objectives, and skill sets.
Data Analyst vs Data Scientist
Here’s an overview of the differences between the two roles.

The primary distinction between a data analyst and a data scientist lies in the scope of their work and job objectives. While data analysts focus on analyzing existing datasets to provide actionable insights, data scientists develop more complex models and algorithms to predict future trends. Data scientists typically have a stronger background in computer science and modeling techniques.
If you’re interested in more details, here are 7 data analyst vs data scientist differences.
Data Analyst vs Business Analyst
Now, let’s have a look at the differences between data analysts and business analysts.

While both roles involve analysis, a data analyst primarily focuses on handling data, performing statistical analysis, and reporting findings. In contrast, a business analyst focuses more on the business implications of data, working closely with stakeholders to translate business needs into technical specifications for IT projects.
Data Analyst vs BI Analyst
Data analysts are often confused with BI analysts. Here’s the overview of the differences for a quick reference.
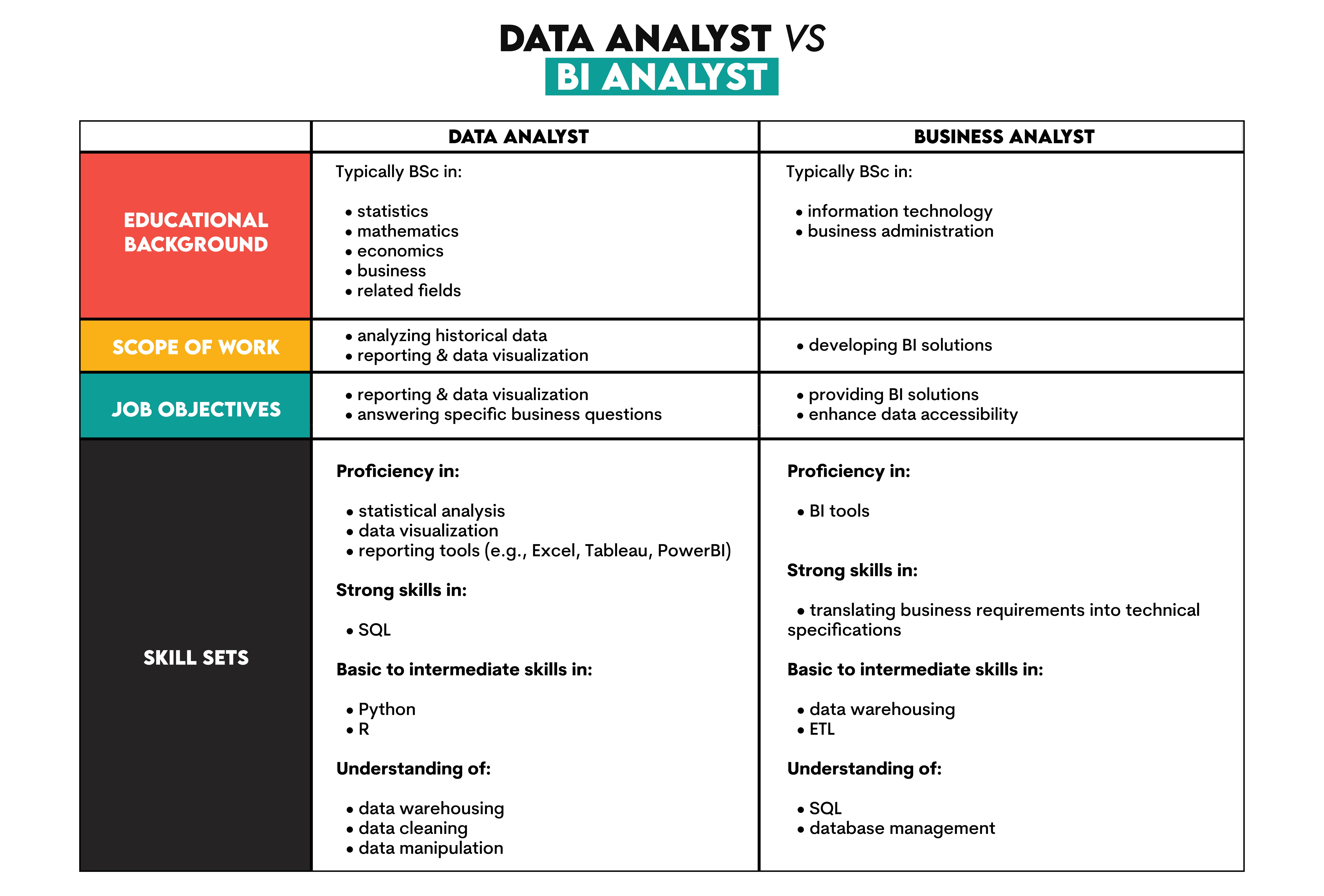
While both roles aim to leverage data to support business objectives, data analysts focus more on the technical aspects of data manipulation and analysis, whereas BI analysts concentrate on the aggregation, presentation, and strategic application of data through BI solutions.
Career Path and Progression
A data analyst career is very dynamic, so it offers many opportunities for professional development.
Here’s what this path typically looks like.
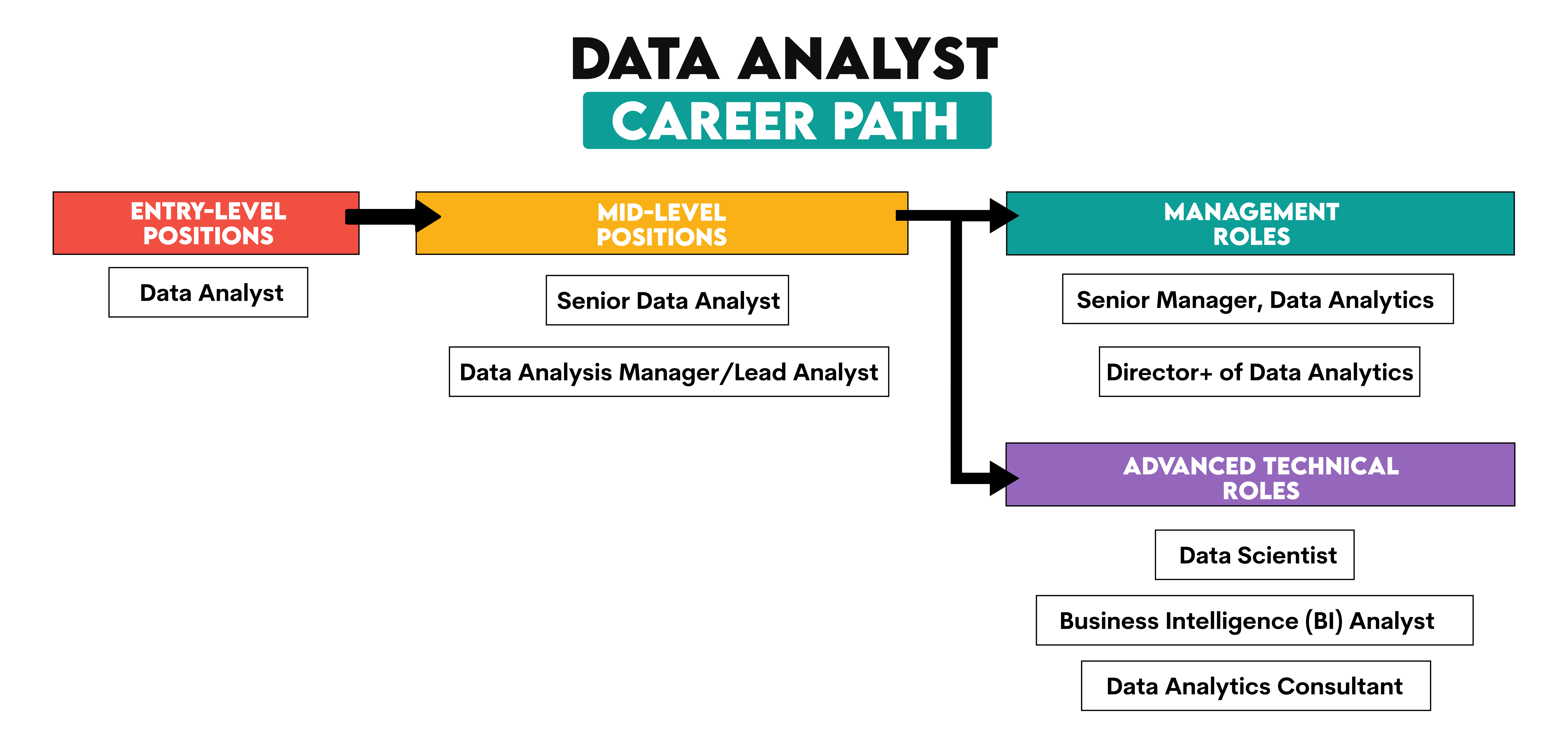
Data analysts start at entry-level positions and then advance to mid-level positions.
After that, the career typically branches out into two directions: management roles and advanced technical roles.
Let’s explore each career stage.
Entry-Level Positions
Data Analyst
Data analysts' careers typically start with entry-level positions, where their primary responsibilities include data collection, cleaning, basic analysis, and reporting.
At this stage, analysts gain hands-on experience with databases, analytics tools, and visualization software.
Mid-Level Positions
Senior Data Analyst
With experience, data analysts can move into senior roles, taking on more complex projects and often managing larger datasets. They might also begin to specialize in certain industries or types of analysis, e.g., marketing, financial, health, or operation analytics.
Senior analysts play a key role in guiding business decisions through more sophisticated data modeling and analysis techniques.
Data Analysis Manager/Lead Analyst
Career progression can lead to managerial positions where the focus shifts towards leading a team of analysts.
Responsibilities include project management, strategic planning, and liaising between the data team and other departments or stakeholders.
While this role has some managerial responsibilities, you’re still heavily involved in the day-to-day aspects of data analysis. Think of this position as something between a technical and management role.
Management Roles
After reaching mid-level positions in data analysis, you can choose to go into management direction. Here your technical skills will become less important as you will focus on overseeing teams, projects, and strategic initiatives.
Senior Manager, Data Analytics
In this role, you are responsible for leading a team of data analysts and overseeing complex analytics projects. You ensure that data analysis aligns with the organization's strategic goals, provide guidance on technical challenges, and manage stakeholder relationships.
Senior managers in data analytics also play a key role in developing and implementing data strategies that drive business value.
Director+ of Data Analytics
A director+ of data analytics takes on a higher level of responsibility, overseeing the entire data analytics function within an organization. This includes setting the strategic direction for how data is used to inform decision-making, ensuring data quality and integrity, and leading cross-functional projects that rely on data insights.
They also manage budgets, develop talent within the analytics team, and foster a data-driven culture across the organization.
Advanced Technical Roles
If you don’t fancy going into management, it doesn’t mean you have to stay in the mid-level positions. You can stay on the technical track. However, this means developing some additional technical skills that are usually not used in data analysis. With that, you can move into technically more advanced roles.
Data Scientist
Data analysts with strong statistical, programming, and analytical skills may progress to become data scientists.
This role involves more complex data modeling, predictive analytics, and machine learning, requiring advanced statistics, mathematics, or computer science education. The role comparison section above provides more details.
Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst
Data analysts might also evolve into BI Analysts, focusing on developing and managing BI solutions, dashboards, and reports to help businesses make strategic decisions.
This role requires a deep understanding of business processes and BI tools. The role comparison section above provides more details.
Data Analytics Consultant
Experienced analysts can become consultants, working with various businesses to solve specific problems, improve data practices, or implement new data systems.
This role often involves a mix of technical skills, business acumen, and communication abilities.
An important part of career progression is also a salary increase. Even the beginner’s salary is quite high, which also makes this career very attractive. You can find more details in our article about data analyst salary.
Conclusion
If you’re interested in working with data, then data analyst is a perfect job for you. Not only can you advance further in data analysis, but this job also potentially allows you to transition into some other data roles.
This article gives you everything you need about the role. Now, it’s on you to prepare for data analyst interview questions and get a job.
Share


