The Essential Role of a BI Analyst in Today's Business World

Categories
BI analysts are essential in data-driven decision-making. Learn what BI is and how you can, too, become that missing piece in your new employer’s data team.
Business intelligence (BI) is in some more knowledgeable circles referred to as ‘that thing that completely changed how businesses make decisions; we need it pronto!’
The ‘thing’ here is a by-product of the surge in overall digitalization and collecting data about everything everywhere all at once.
One could argue that BI is the reason why businesses started collecting data in the first place. After all, most companies’ goal is to earn more, and BI makes that possible.
Introduction to Business Intelligence (BI) and Its Significance
BI refers to technologies, applications, strategies, and practices used to collect, analyze, integrate, and present business information. This very dull definition wants to say that BI uses technology to sift through mountains of data, turn it into golden nuggets of information, and use nice visualizations to present it to decision-makers.
Business intelligence is eyes to decision-makers. Without it, they can only tap in the dark and hope their next step will lead them where they want to go.
So, there it is – the significance of business intelligence!
The Evolution of Business Intelligence
Business intelligence is much older than you might think.
The term ‘business intelligence’ first appeared in Richard Millar Devens’ ‘Cyclopædia of Commercial and Business Anecdotes’ in 1865.
BI is mentioned in the context of the English banker’s success: ‘Throughout Holland, Flanders, France, and Germany, he maintained a complete and perfect train of business intelligence. The news of the many battles fought was thus received first by him, and the fall of Namur added to his profits, owing to his early receipt of the news.’
According to this quote, the author claims that collecting information and reacting accordingly based on it is the core of business intelligence.
No wonder that this quote appears in the years after the First Industrial Revolution. It was the birth of modern capitalism, and even then, it was obvious that having better and more information than your competitors is crucial.
Today, we’re collecting much more data using more sophisticated tools (computers), and we’re better at analyzing it and gaining insights. But, the underpinning principles are the same – get some data and make decisions based on it.
In the modern context, developing relational databases in the 1960s was a crucial moment. Very broadly, modern BI history after that can be watched through three stages. Mind you, they are not necessarily linear and exclusive, i.e., all three types of BI do exist today. I’m speaking more about trends here.
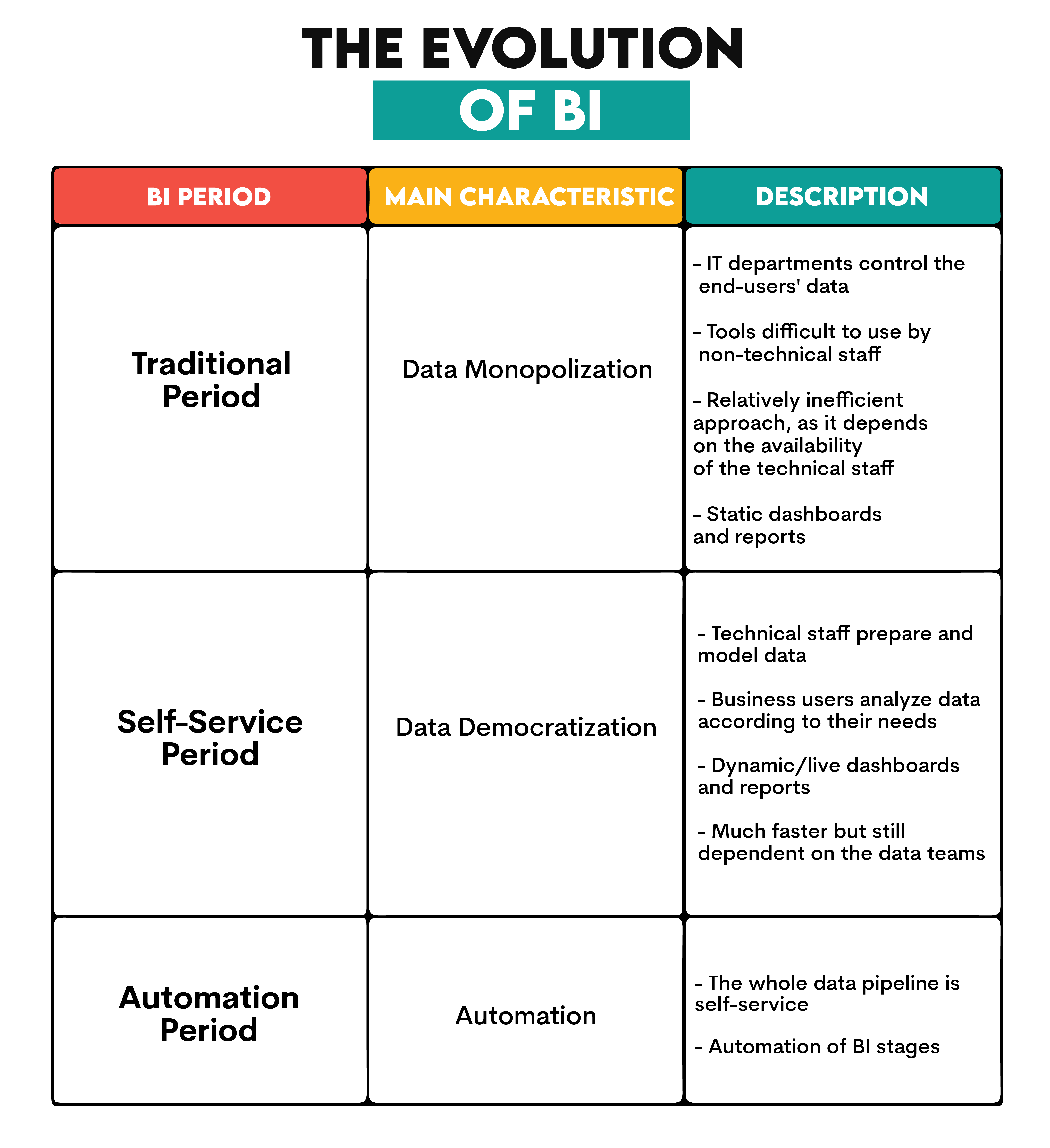
BI Cycle
You read that wrong; it’s a BI cycle, not a bicycle. While bicycles can be important transportation modes for some BI analysts somewhere (Amsterdam, I’m looking at ya!), BI cycles have a different purpose: understanding the BI analyst’s role.
The BI cycle kicks off by realizing there’s a business problem and clearly defining it. In other words, this stage identifies specific business questions that BI will try to answer.
Next comes collecting data from various sources, including internal systems like sales and marketing databases and external sources such as market research and social media.
Once you get it, you need to prepare data by cleaning, transforming, and organizing it. This is done to address inaccuracies, missing values, and inconsistencies. Additionally, data needs to be modeled or structured to support efficient analysis. This involves creating schemas that define the relationships between different data elements.
After that, data is stored in a data warehouse or other storage. This stage ensures data is organized, scalable, and secure so data access and analysis can be efficient.
To gain insights, data needs to be analyzed by applying data mining and statistical techniques, and machine learning algorithm. In this stage, patterns, correlations, and trends are identified.
The insights are presented in a visual manner, which involves charts, graphs, and dashboards. This way, data analysis is easily communicated to decision-makers, who tend to be non-technical.
Finally, these decision-makers close the BI cycle by making decisions based on the presented information.
What Does a BI Analyst Do?
BI analysts are fully involved in all BI stages except the first and the last. The extent to which they’re involved can depend on the organization's structure, the BI processes' complexity, and the individuals' skills.
Generally, the BI analyst's job consists of these tasks.
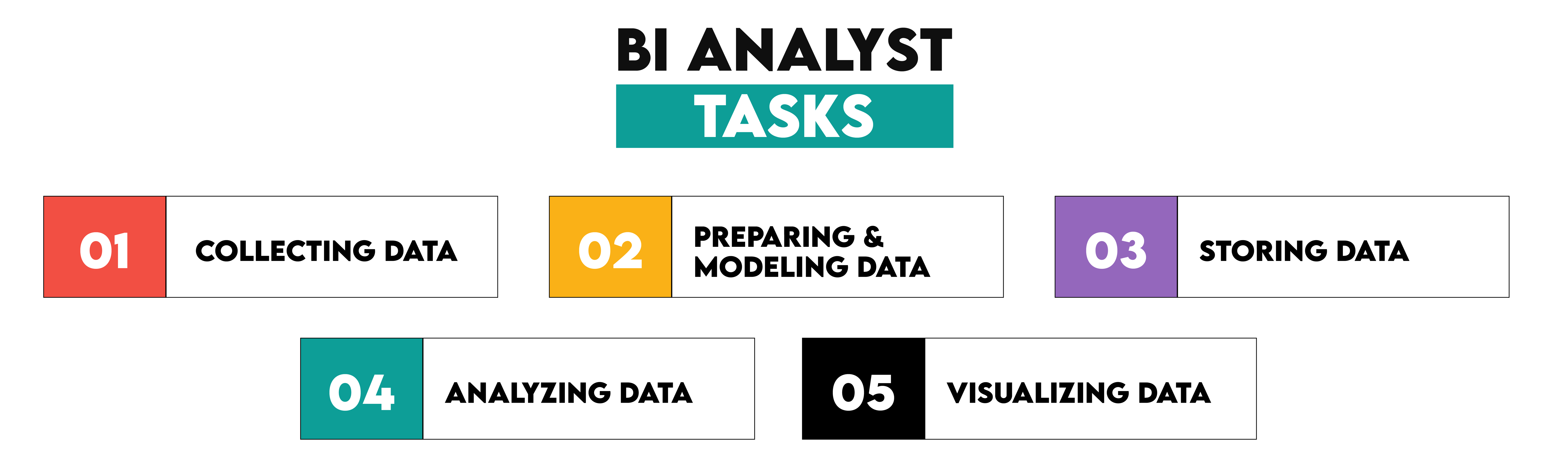
Typically, collecting data belongs to data engineers’ or IT specialists’ tasks, as their role is to set up and maintain the data collection infrastructure. As for BI analysts, they often contribute by specifying data requirements and ensuring that the collected data aligns with the business problems defined. However, depending on the organization, BI analysts can own data collection entirely.
On the other hand, BI analysts are heavily involved in preparing and modeling data.
When it comes to storing data, this is usually handled by data engineers and database administrators. BI analysts, however, may help design the data architecture and ensure that the data storage solutions meet the analysis needs.
Analyzing data is the BI analyst’s core task, as they are experts in interpreting data in the business context and identifying trends, patterns, and anomalies.
BI analysts are also usually responsible for visualizing data. They’ve done data analysis, so they’ll know best how to make their insights accessible, presentable, and understandable.
Key Skills and Tools for a BI Analyst
To do all these tasks, BI analysts must have a unique set of skills: a mix of data management, analytical, technological, and soft skills
Technical Skills
The details of these skills are presented below.

Technological Skills
These skills mean the BI analyst can use the most common BI tools and software. Tools can be divided into two categories.
The BI and data visualization tools are used for data analysis, visualization, and reporting. Some of the most common tools in this category include:
- Tableau
- Power BI
- QlikView/Qlik Sense
- Looker Studio (formerly Google Data Studio)
Regarding the advanced analytics software, you should know some of these tools:
- SAS
- SPSS
- Python libraries
- pandas – data manipulation and analysis
- NumPy – numerical computing
- scikit-learn – ML library
- statsmodels – statistical modeling and hypothesis testing
- TensorFlow – ML and DL library
- Keras – API for building and training DL models
- PyTorch – ML and DL library
- XGBoost – gradient boosting library
- LigthGBM – gradient boosting library
Business Skills
The word ‘business’ is in the Business Intelligence Analyst’s name for a reason! To be successful in this job, you need to have strong business skills.
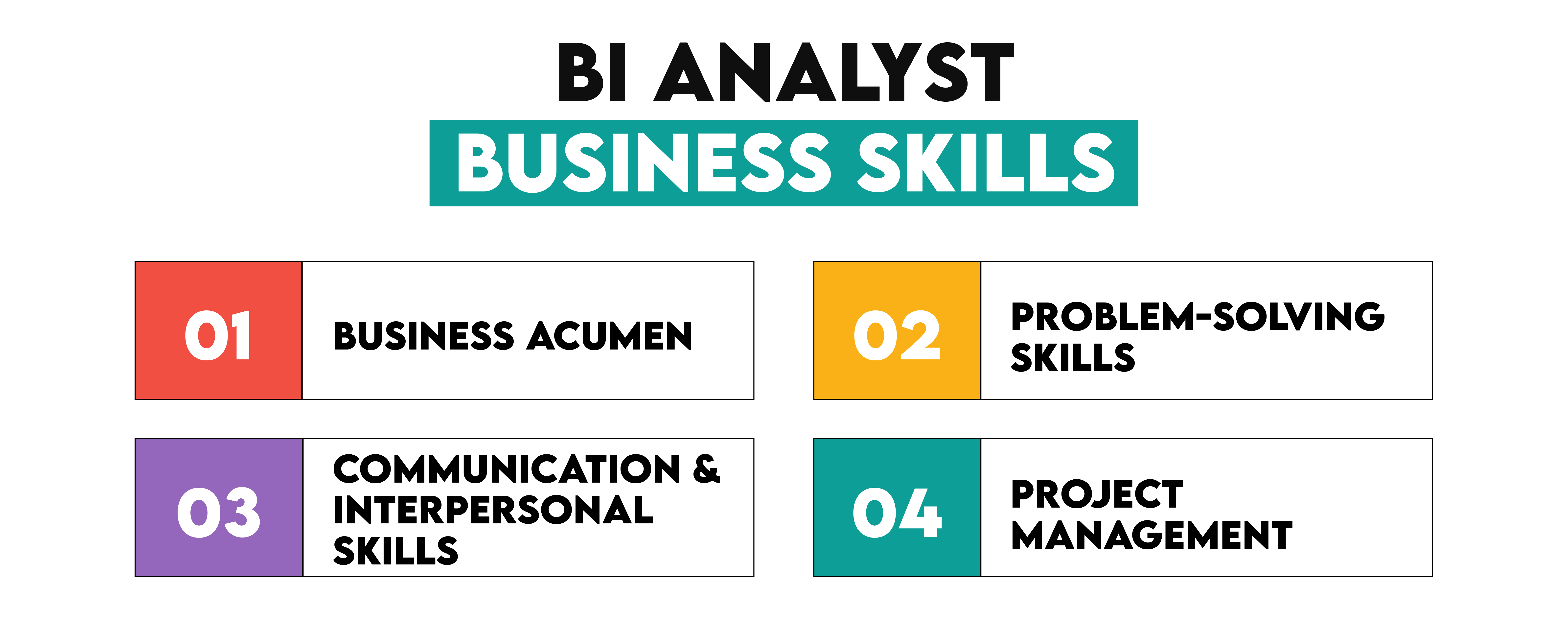
- Business Acumen: Understanding the business context is crucial for BI analysts. They must grasp the industry dynamics, business processes, and how data impacts business decisions and strategies
- Problem-Solving Skills: As a BI analyst, you should be adept at identifying business problems and using data to propose viable solutions. This involves critical thinking and the ability to approach problems from multiple angles.
- Communication and Interpersonal Skills: BI analysts must communicate complex ideas clearly and effectively to non-technical stakeholders. This includes writing reports, giving presentations, and collaborating across departments.
- Project Management: This is not their core domain. However, project management skills help BI analysts oversee projects from inception to completion, ensuring they meet business requirements and deadlines.
Soft Skills
As with every job today, soft skills also shouldn’t be neglected.
- Attention to Detail: Due to the complexity and volume of data BI analysts usually handle, they must be attentive to detail to spot trends, anomalies, or inconsistencies in data.
- Curiosity and Continuous Learning: As with every data field, business intelligence is also a constantly evolving field. To keep pace, BI analysts should be committed to continuous learning and staying abreast of new technologies, tools, and practices.
- Adaptability: Today’s business world is increasingly volatile and changing. BI analysts must adapt to the changes in business needs, technologies, and data sources.
BI Analyst Salary
Your salary will, of course, depend on your experience, location, company, and negotiation skills. We can’t take account of every individual case, but we can talk about the averages.
To get the BI analyst’s average salary, we will take into account three relevant salary source sites: Glassdoor, levels.fyi, and Indeed. They differ only slightly, so we can confidently say that your total compensation as a BI analyst in the US will be around $100,000.
Let’s shortly analyze each salary data source.
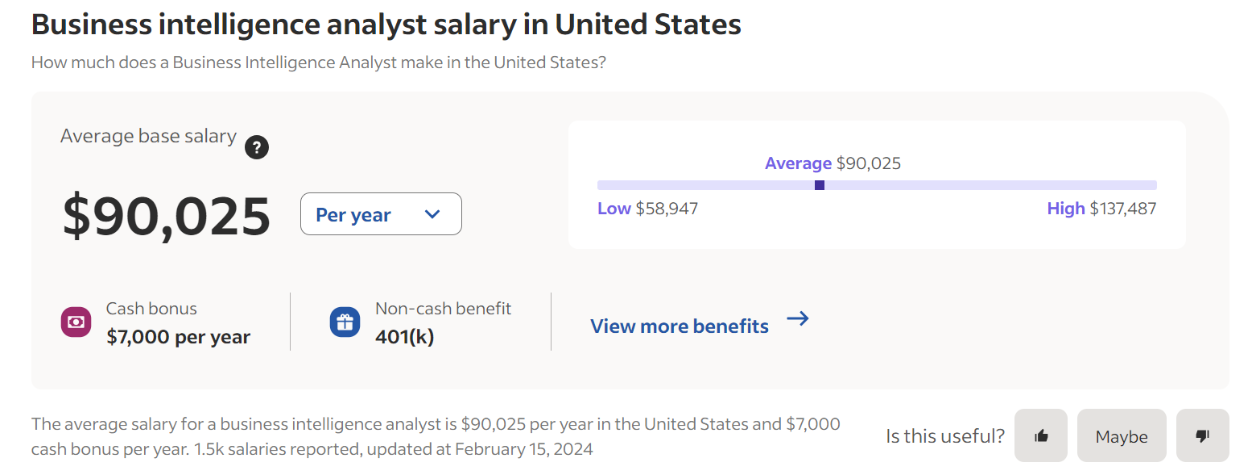
Data from Glassdoor tells us that the total pay is between $80k and $115k. It consists of base pay ($76k - $106k) and additional pay ($5k - $9k). The average base salary is $89k, while the average total pay is $96k.
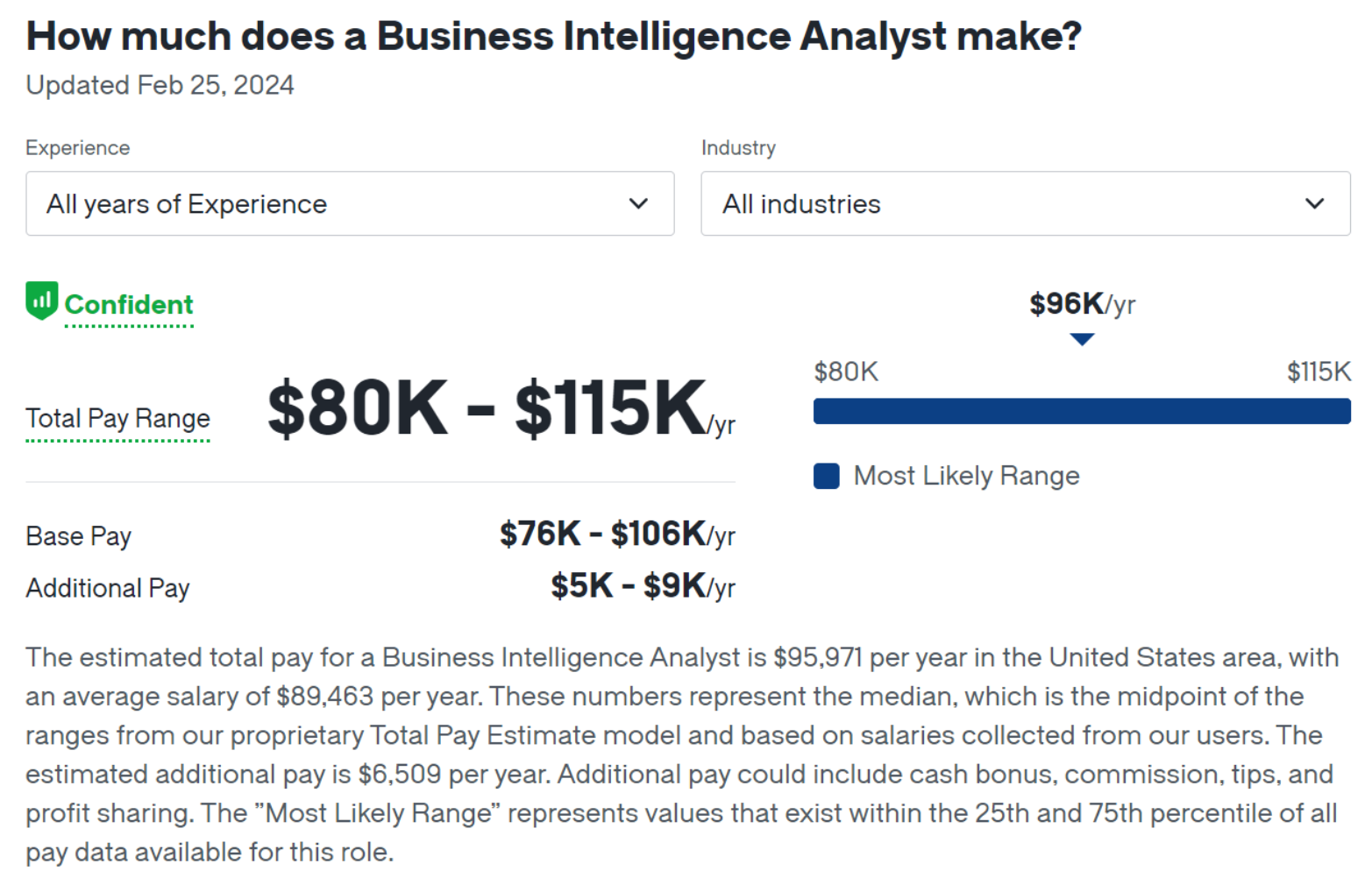
The info from levels.fyi shows the median total salary at $110k. It’s worth noting that 75% of BI analyst salaries are below $140k, while 90% are below $180k.
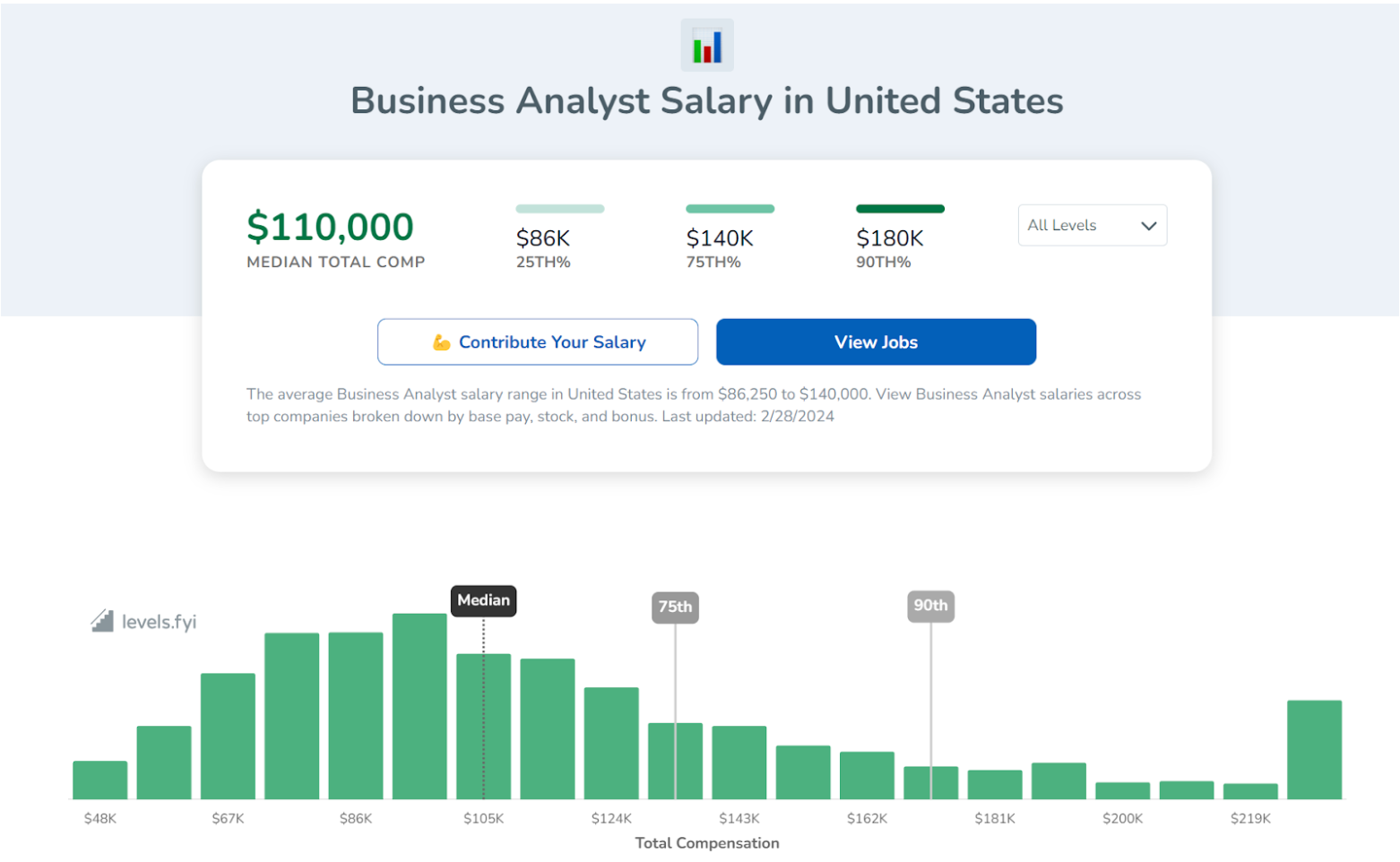
Indeed’s data shows only base salary as the average. It amounts to $90k. However, if we add the cash bonus reported at $7k, this gives a total pay average of around $97k. This is almost the same as the average reported by Glassdoor.
How to Become a Business Intelligence Analyst
Becoming a BI analyst technically includes only one step: being hired for a BI analyst position. But how do you make yourself a desirable candidate? This requires a combination of education, skills development, and practical experience.
These are the general steps you can take toward the BI analyst career.
Relevant education might include (at least) a bachelor’s degree in relevant fields such as Information Technology, Computer Science, Statistics, Business Administration, or a related area.
You can also take specialized (online) courses. The courses and certifications can focus on a certain subject area or a tool. Here are some online suggestions:
- Business Analytics Specialization (Coursera)
- Data Visualization With Tableau Specialization (Coursera)
- Excel to MySQL: Analytic Techniques for Business Specialization (Coursera)
- Complete Introduction to Microsoft Power BI (Udemy)
- Qlikview Developer (Udemy)
- SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence (BI) 4.2 - SAP BO (Udemy)
- SQL for Data Science (Coursera)
- Database Design and Management (Udemy)
- HarvardX: Statistics and R (edX)
- Python for Data Science and Machine Learning Bootcamp (Udemy)
- Business Strategy Specialization (Coursera)
- Strategic Business Analytics Specialization (Coursera)
- Certified Business Intelligence Professional (CBIP) (TDWI)
- Microsoft Certified: Power BI Data Analyst Associate (Microsoft)
Regarding practical experience, you can gain it by looking for internships. Another option is using various platforms to practice coding technical skills and work on projects. Some of the platforms are:
Potential employers need to see your skills. Building a portfolio consisting of reports, dashboards, and projects that highlight your BI skills is the best way to do that.
Challenges of BI Analysts
As with every job, BI analysts, too, face certain challenges that make their lives difficult.

Data Quality and Consistency: BI analysts often deal with data that is incomplete, inaccurate, or inconsistent, with discrepancies between different data sources. All this must be resolved before analysis, as inconsistent and poor-quality data will probably lead to misleading insights. And these are not insights at all!
- Data Integration and Silos: Companies typically store data across different systems and departments, creating data silos. The challenge here for BI analysts is to integrate these data into a cohesive, unified view.
- Data Security and Privacy: Increasing concerns about data breaches and privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR and CCPA) show that data security and privacy will be – if they’re not already – one of the central concerns of BI analysts. They have to navigate legal and ethical considerations while managing sensitive information. This requires a detailed understanding of data governance and security best practices.
- Real-Time Insights: The development of technology brought the possibility of real-time or near-real-time insights. This adds pressure to BI analysts, along with the increased necessity of managing big data.
- Job Market: This is not exclusive to BI analysts, but the current data job market shows fewer job openings compared to hey-days of pre-COVID and COVID period. This doesn’t mean there are no jobs there. There are, but, to land them, data professionals need to specialize. A positive here is that BI analysis is a specialization already. However, it probably won’t hurt you to specialize even more, depending on your strongest skills and experience. You can focus on one part of BI and become a specialist in that, or become an industry-specific BI analyst.
Future of BI and the Role of Analysts
There was a period in history where, compared to today, there was too little data to make decisions on it. Now, it seems we’re on the other end: there’s too much data to make any sense of it!
This is where the future of BI and BI analysts lies: employing technological advances that make it possible to handle ever-increasing mountains of data and keep delivering valuable insights to decision-makers.
Though BI analysts already do that, in the future, their focus will be even more on using large-language models (LLMs), generative AI, and NLP to analyze data and dig out useful insights, even automating data-driven decision-making. So, today’s BI analysts would be wise to start getting familiar with these fields.
I already mentioned the relatively new possibility of delivering real-time insights. Demand for that will increase, and with that, the BI analysts will be required to up their skills in big data mining.
With this comes the focus on BIaaS (Business Intelligence-as-a-Service), as it allows for handling huge amounts of data within an easily implementable solution. They allow for collaboration and integration within the currently existing business systems and workflows, enabling the users to derive insights without extensive help from the data team.
Conclusion
In recent years, BI and BI analysts have been a driving force behind the rise of data-driven organizations. Their unique mix of data management, analytical, technological, and soft skills became very valued in the job market. Their average salary of $100,000 is a testament to that.
The importance of BI analysts will only increase in the future as we enter the period of ‘unmanageable’ amounts of available data. In the said future, which is already here, even more focus will be put on BI analysts' technical skills, like coding, machine learning, and AI. Avoid being left behind by delving into these skills with our SQL, Python, and R coding questions and non-coding questions that include business and product questions. You can expand all the skills you learn by adding our data projects to your portfolio.